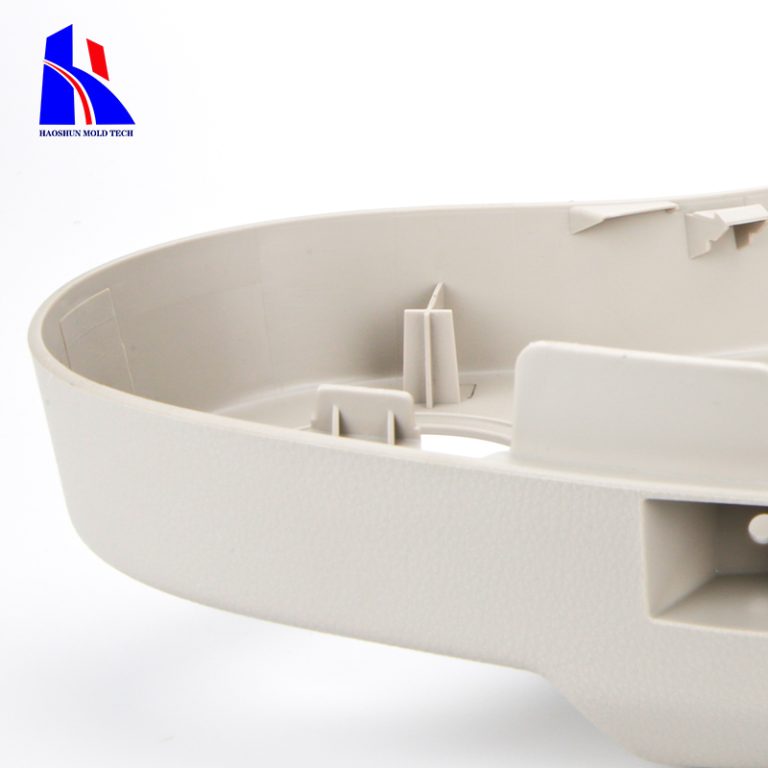
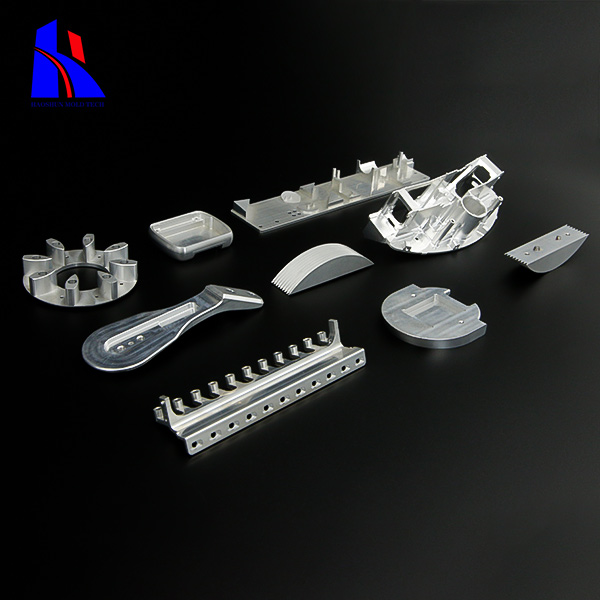
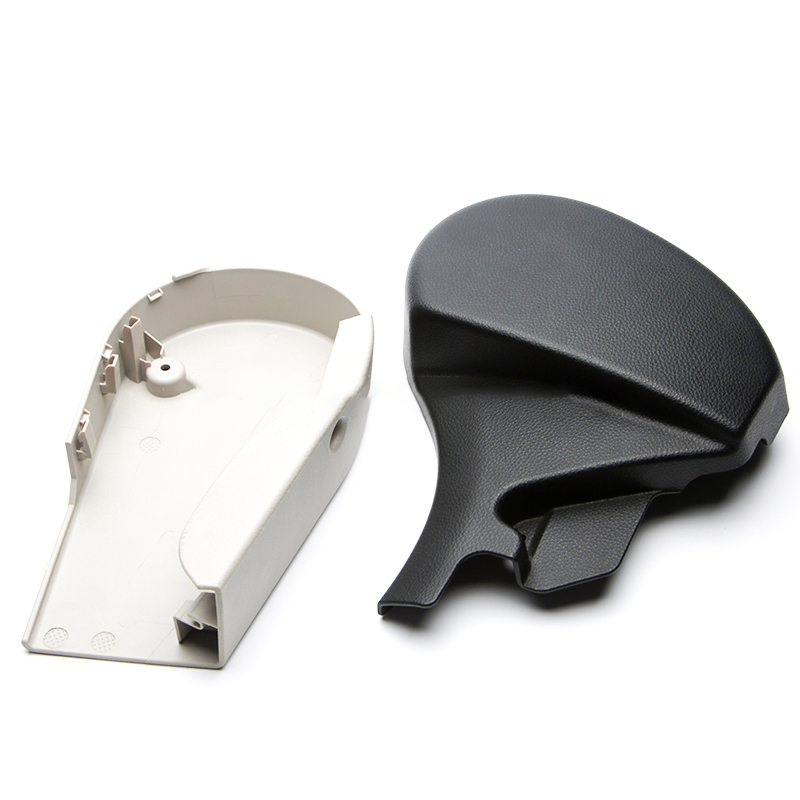
plastic production parts abs injection molded plastic parts
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a popular thermoplastic polymer used in a wide range of applications, particularly in injection molding. This material is favored for its impact resistance, strength, and ease of processing. Here’s a detailed look at ABS injection-molded plastic parts:
ABS Injection-Molded Plastic Parts

- Overview of ABS
1.Composition: ABS is a copolymer composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene. The combination of these components imparts desirable properties such as high impact resistance, toughness, and stability.
2.Properties:
3.Impact Resistance: High resistance to impact and shock, making it ideal for durable parts.
4.Strength: Good tensile strength and rigidity.
5.Thermal Stability: Can withstand a moderate range of temperatures.
6.Chemical Resistance: Resistant to acids, alkalis, and some solvents.
7.Ease of Fabrication: Good flow properties during molding.
- Injection Molding Process
8.Preparation:
9.Material Drying: ABS pellets are typically dried before processing to remove any moisture that could affect the quality of the molded parts.
10.Mold Design: The mold design includes the cavity and core that form the final shape of the part. The design must account for factors like part geometry, wall thickness, and draft angles.
11.Injection:
12.Melting: ABS pellets are heated in the barrel of the injection molding machine until they melt into a viscous liquid.
13.Injection: The molten ABS is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The pressure ensures that the mold fills completely and that the part takes on the desired shape.
14.Cooling:
15.Solidification: The molten ABS cools and solidifies within the mold. The cooling time is crucial for achieving the desired mechanical properties and dimensions.
16.Ejection:
17.Removal: Once cooled, the molded part is ejected from the mold. The design of the mold often includes features like ejector pins to facilitate this process.
- Applications of ABS Injection-Molded Parts
ABS is used in a variety of applications due to its versatility:
18.Consumer Electronics: Enclosures for devices like computers, smartphones, and TVs.
19.Automotive: Interior and exterior components such as dashboards, trim, and panels.
20.Toys: Parts for various types of toys, including LEGO bricks.
21.Appliances: Components for household appliances like refrigerators and washing machines.
22.Medical Devices: Some medical device housings and components.
- Advantages of ABS Injection Molding
23.High Production Efficiency: Injection molding allows for the rapid production of parts with high precision.
24.Design Flexibility: Complex shapes and intricate details can be achieved.
25.Consistency: The process ensures uniformity in part dimensions and quality.
26.Cost-Effectiveness: Suitable for high-volume production with reduced per-part costs.
- Considerations and Challenges
27.Temperature Sensitivity: ABS can deform under high temperatures, so it might not be suitable for all high-temperature applications.
28.Environmental Impact: While ABS is recyclable, its production involves petrochemicals and may have environmental impacts.
29.Surface Finish: The surface finish of molded parts can vary based on mold design and processing conditions.
- Maintenance and Quality Control
30.Tool Maintenance: Regular maintenance of the mold and injection machine is necessary to ensure consistent quality and avoid defects.
31.Quality Control: Inspection of parts for dimensional accuracy, surface defects, and mechanical properties is essential to maintain product standards.
In summary, ABS injection-molded plastic parts are valued for their robustness, ease of processing, and versatility. The injection molding process enables the production of complex and precise parts efficiently, making ABS a popular choice in various industries.
email : shine@haoshuntech.com
telephone: +8613560008062