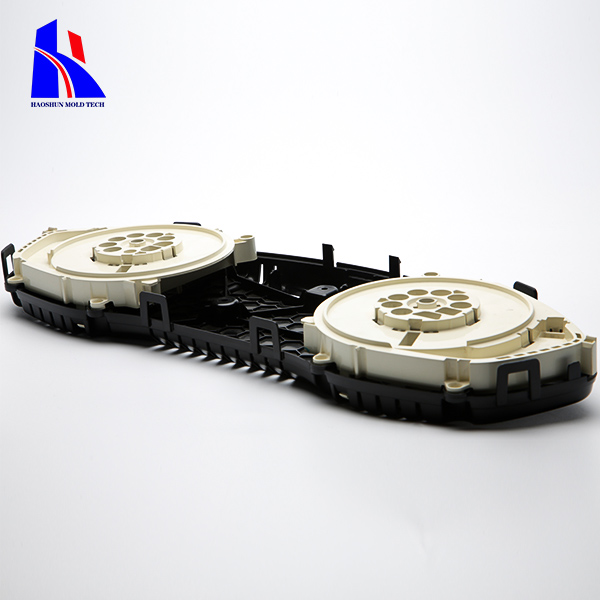
plastic parts manufacturer plastic parts manufacturing
Manufacturing plastic parts involves a range of processes and technologies designed to produce high-quality components used in various industries. Here’s a detailed overview of the plastic parts manufacturing process, including key methods, considerations, and applications:
- Plastic Parts Manufacturing Processes
Injection Molding
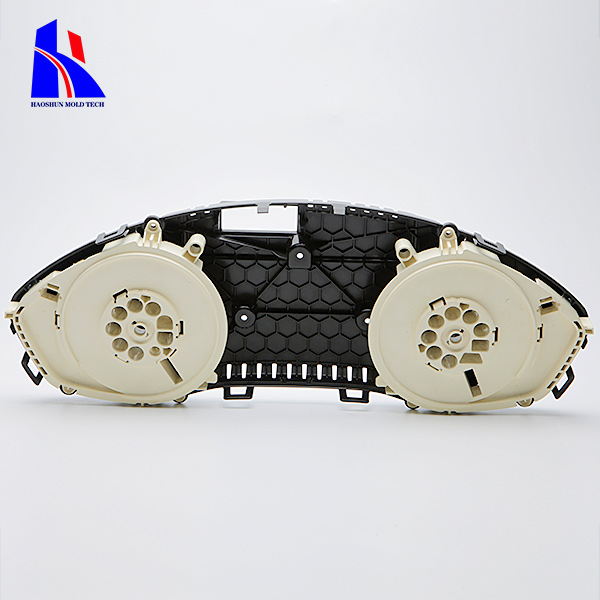
1.Description: This is the most common method for producing plastic parts. Plastic material is heated until it melts, then injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The plastic cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold.
2.Advantages: High precision, repeatability, and efficiency for large production runs. Capable of producing complex shapes with tight tolerances.
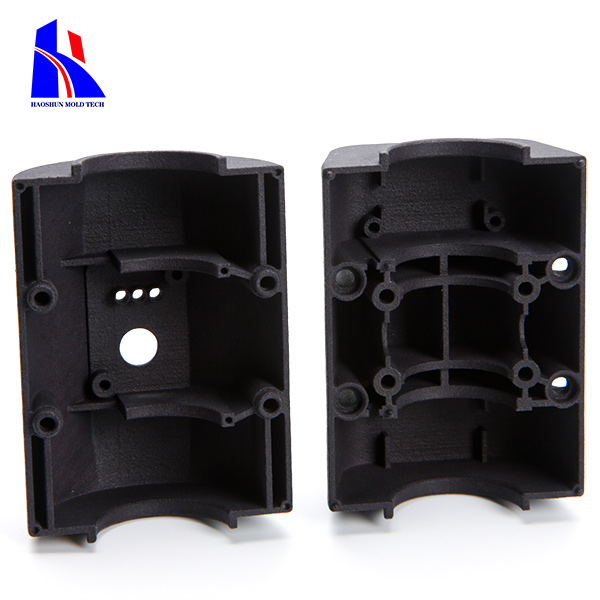
3.Applications: Automotive parts, consumer goods, medical devices, and electronics.
Blow Molding
4.Description: Used to produce hollow plastic parts. A tube of molten plastic (parison) is inflated inside a mold to form the part.
5.Advantages: Ideal for producing large, hollow parts like bottles and tanks.
6.Applications: Bottles, containers, and large hollow components.
Rotational Molding
7.Description: Plastic powder is placed into a mold, which is then rotated around two axes while being heated. The powder melts and coats the mold interior to form a hollow part.
8.Advantages: Good for producing large, hollow, and seamless parts.
9.Applications: Playground equipment, storage tanks, and large containers.
Extrusion
10.Description: Plastic is melted and forced through a die to create long shapes with a consistent cross-section, which are then cut to the desired length.
11.Advantages: Efficient for producing continuous lengths of plastic profiles.
12.Applications: Pipes, tubing, and window frames.
Thermoforming
13.Description: Plastic sheets are heated until soft, then formed over a mold using vacuum, pressure, or mechanical force. The plastic is then trimmed and finished.
14.Advantages: Suitable for low to medium volume production with less tooling cost compared to injection molding.
15.Applications: Packaging, automotive panels, and appliance housings.
- Key Considerations in Plastic Parts Manufacturing
Material Selection
16.Plastics: Various types including thermoplastics (e.g., ABS, PVC, polycarbonate) and thermosetting plastics (e.g., epoxy, phenolic).
17.Properties: Strength, flexibility, temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and appearance.
Design and Engineering
18.Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Ensuring the part design is optimized for the chosen manufacturing process to avoid issues like warping, shrinkage, or poor surface finish.
19.CAD and Simulation: Using computer-aided design (CAD) and simulation tools to model and test designs before physical production.
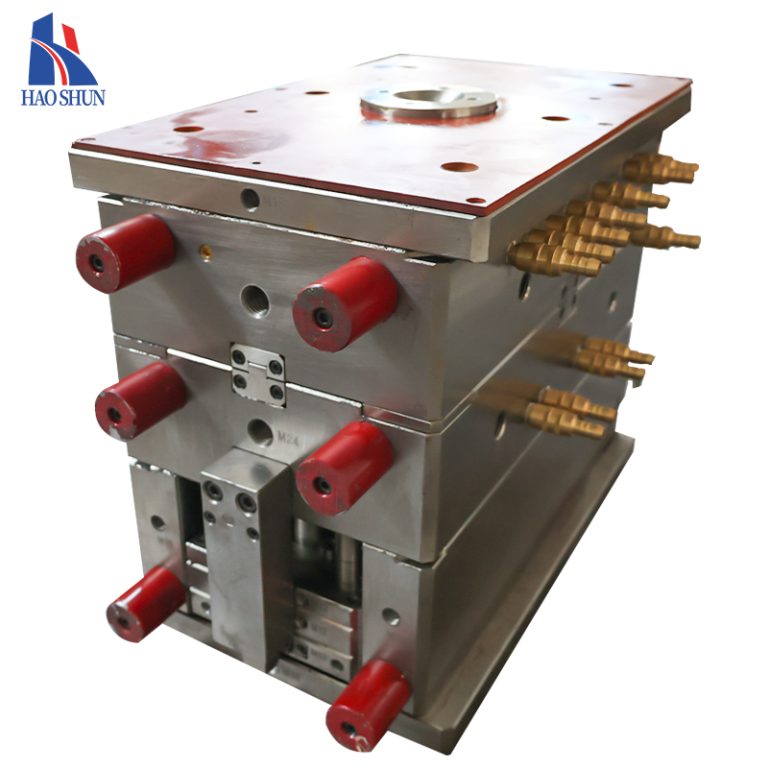
Tooling and Molds
20.Tooling Costs: Investment in molds and dies can be significant, especially for complex parts.
21.Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to ensure molds and tools remain in good condition.
Quality Control
22.Inspection: Ensuring parts meet dimensional, functional, and aesthetic requirements through various inspection techniques.
23.Testing: Mechanical testing, chemical testing, and performance testing to ensure parts meet specifications.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
24.Recycling: Using recyclable plastics and implementing recycling processes for waste material.
25.Energy Efficiency: Optimizing manufacturing processes to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Applications and Industries
26.Automotive: Parts such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior components.
27.Medical: Devices and components like syringes, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
28.Consumer Goods: Household items, toys, and appliances.
29.Electronics: Enclosures, connectors, and insulation components.
30.Industrial: Machinery parts, containers, and equipment.
- Future Trends in Plastic Parts Manufacturing
31.Advanced Materials: Development of new materials with enhanced properties, such as biodegradable plastics and composites.
32.Automation: Increased use of robotics and automation for efficiency and precision in manufacturing processes.
33.3D Printing: Growing use of additive manufacturing technologies for prototyping and low-volume production.
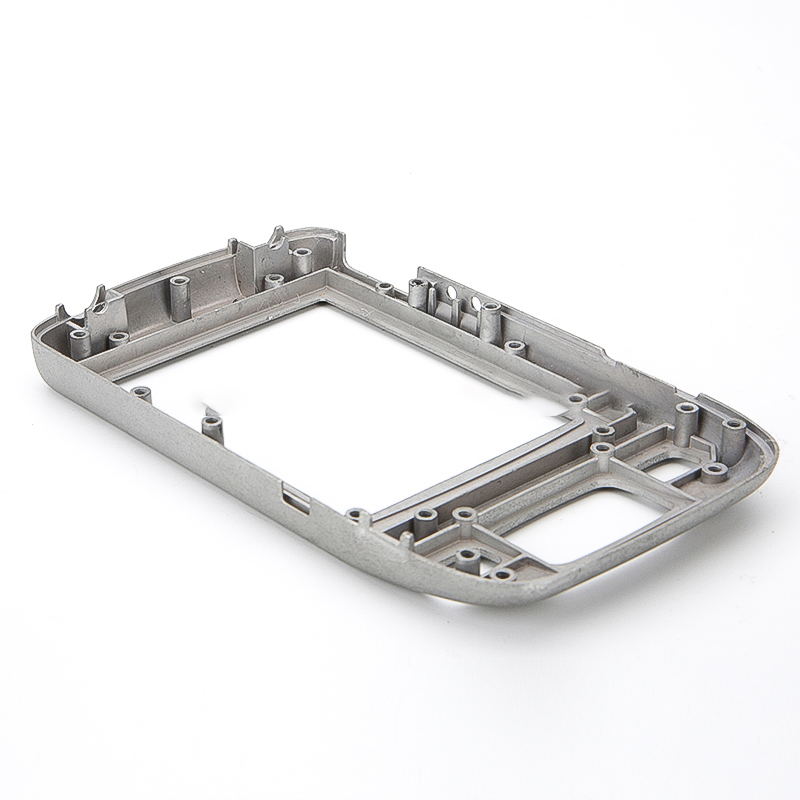

In summary, plastic parts manufacturing is a complex and versatile field that leverages various techniques to meet the needs of different industries. The choice of process and material depends on factors such as part complexity, production volume, and functional requirements. Advances in technology and materials continue to drive innovation in this industry.
email : shine@haoshuntech.com
telephone: +8613560008062